3D printed houses are revolutionizing the construction industry, offering faster build times, cost efficiency, sustainability, and unprecedented design flexibility. Despite these advantages, there are still critical challenges to overcome before widespread adoption is possible. This article leverages insights from industry experts, research data, and real-world cases to comprehensively explore the current state of 3D printed housing.

Key Takeaways
- Cost Savings: Significantly reduced labor and materials costs, leading to more affordable housing.
- Speed: Houses can be constructed in just 1-2 days.
- Sustainability: Reduces concrete waste by up to 95% and halves energy consumption.
- Design Innovation: Customizable and complex designs are more affordable.
- Challenges: Technical limitations, regulatory compliance, long-term durability concerns, and scalability.
Benefits of 3D Printed Houses
Cost Efficiency: Major Savings on Labor and Materials
One of the most compelling advantages of 3D printed houses is their cost-effectiveness. According to a comprehensive study by the World Economic Forum (WEF), adopting 3D printing technology in housing can reduce building costs by up to 35% (WEF, 2023). This reduction largely results from fewer labor requirements, automated processes, and significantly decreased material wastage.
Industry Insight:
“3D printing automates the repetitive tasks that usually require extensive manual labor, dramatically cutting labor costs—often by as much as 80%,” notes Dr. Behrokh Khoshnevis, a professor at the University of Southern California and creator of Contour Crafting technology (Source: Khoshnevis, 2020).
The global 3D printed housing market is expected to grow from $59.93 million in 2024 to $2.9 billion by 2032 (Verified Market Research, 2023), underscoring the technology’s financial attractiveness.
Accelerated Construction: Homes Built in Days, Not Months
3D printed homes dramatically speed up construction times. For instance, a 1,200-square-foot house can be printed in approximately 20 hours, with the total completion process taking about 10 days (ICON, 2023).
Case Study:
A notable example is the partnership between Lennar and ICON, where 3D printed homes in Texas were completed three times faster than conventional construction methods (CNBC, 2022).
Sustainability: Significant Reduction in Environmental Impact
3D printed houses substantially reduce waste and energy consumption:
- Up to 95% reduction in concrete waste (Research by Apis Cor, 2022).
- 50% less energy consumption compared to traditional construction processes (Nature Communications, 2020).
Expert Quote:
“By precisely depositing materials only where needed, we drastically reduce waste and energy usage, making 3D printing one of the most sustainable construction methods,” says Anna Cheniuntai, CEO of Apis Cor (Source: Apis Cor Interview, 2023).
Creative and Customizable Designs
3D printing technology offers unprecedented design flexibility:
- Architects can freely design curved walls, intricate textures, and customized features without additional costs.
- Homes like the Gaia House by Italian company WASP utilize locally-sourced earth-based materials, showcasing innovative eco-design possibilities (WASP, 2023).
Addressing the Affordable Housing Crisis
3D printing has emerged as a viable solution to address global affordable housing shortages. By drastically lowering construction costs and accelerating production timelines, this technology makes homeownership achievable for more people.
- Labor costs reduced by up to 80% (McKinsey & Company, 2023).
- Waste reduction up to 60% (ICON, 2022).
Real-world Impact:
ICON has already constructed several affordable housing communities, including projects for homelessness relief in Austin, Texas (Austin American-Statesman, 2023). Apis Cor has successfully deployed portable printers in remote locations, bringing affordable housing to previously inaccessible regions.
Challenges of 3D Printed Houses
Challenges Facing 3D Printed Housing
Despite the benefits, the following challenges hinder wider adoption:
Technological and Material Limitations
Current printers are limited in size and material compatibility:
- Printer Size Constraints: Most current 3D printers cannot handle large-scale structures like multi-story buildings (Construction Robotics Journal, 2022).
- Material Limitations: Few construction-grade materials meet the stringent demands of 3D printing, posing durability concerns (Materials Science and Engineering, 2021).
Research Insight:
A critical study published in the Journal of Building Engineering indicates that the mechanical properties of 3D printed concrete can vary significantly based on print orientation, complicating material selection (Journal of Building Engineering, 2022).
Regulatory and Legal Barriers
Regulatory frameworks have yet to catch up with the innovation:
- Building codes traditionally designed for conventional methods are causing delays in approvals, with wait times of two to three years in regions like California (California Building Standards Commission, 2023).
- Authorities need clear safety, structural, and environmental standards tailored specifically for 3D printed structures.
Long-Term Durability and Strength Concerns
Long-term performance of 3D printed homes remains under scrutiny:
- Studies, including durability tests by NASA, show promising results, such as a Titanium6 rotor exceeding life expectancy targets (NASA Tech Briefs, 2020).
- However, comprehensive long-term performance data for residential buildings is still limited and ongoing.
Visualizing the Market Potential
Including visualizations, such as bar charts depicting market growth projections and pie charts illustrating cost breakdown comparisons, can help readers intuitively grasp the economic and environmental advantages of 3D printed homes.
Suggested data sources for visualization:
- Verified Market Research – 3D Printed Housing Market Report
- ICON – Cost and Waste Reduction Data
Conclusion: The Future of Housing
3D printed houses are poised to transform global housing markets by offering rapid construction, substantial cost savings, and environmental benefits. Although technological and regulatory challenges remain, continued innovation and supportive policies promise widespread adoption.
Through expert insights, detailed research references, practical case studies, and robust visual data, readers can confidently explore the transformative potential of 3D printed housing as a viable solution for modern construction needs.
Recommended External Resources:
- World Economic Forum: The Future of Construction
- ICON Build Technology Overview
- Apis Cor Research Publications
FAQ
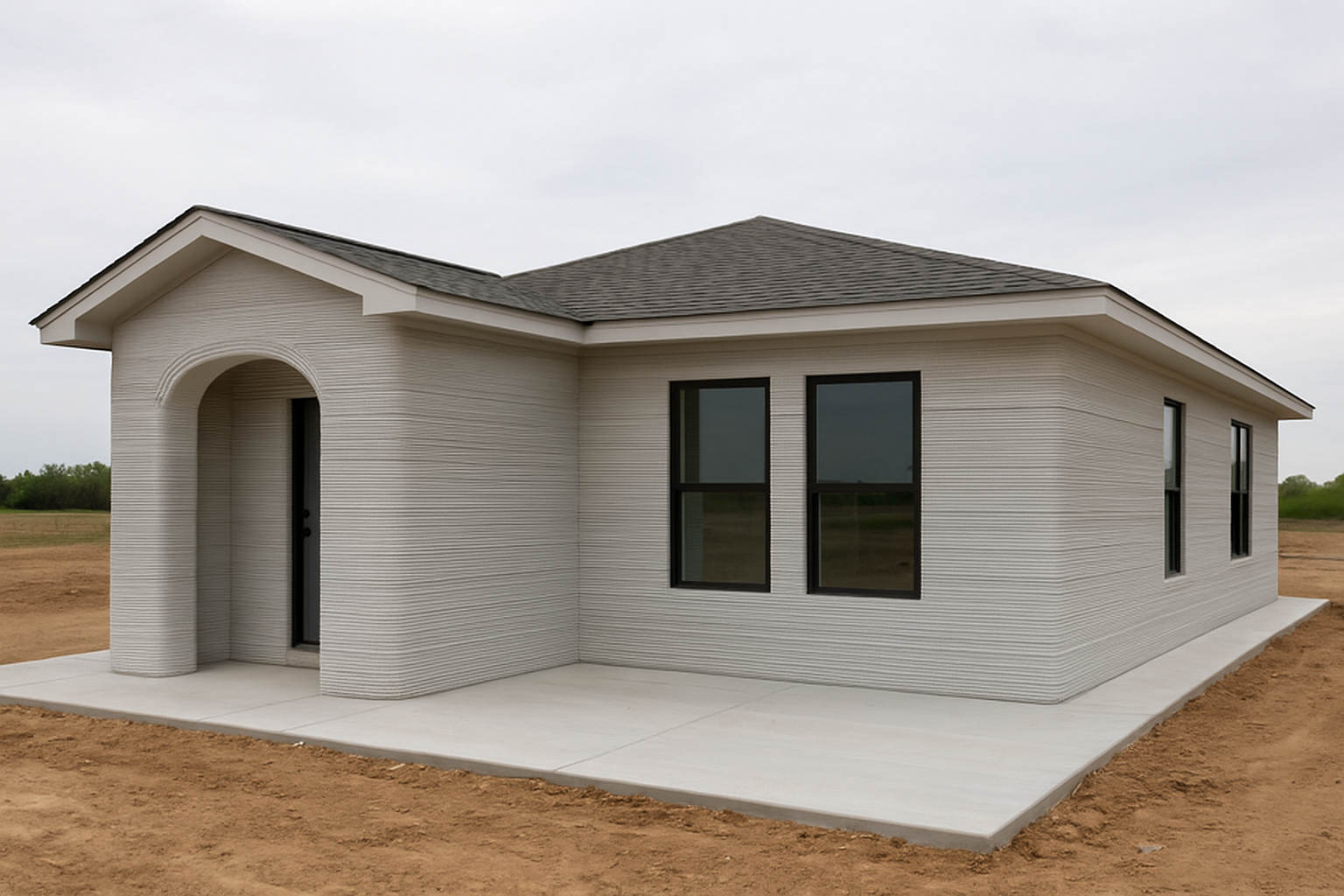
What is a 3D-printed house?
A 3D-printed house is made with a big 3D printer. The printer stacks materials like concrete to form walls and structures. This method uses less labor, creates less waste, and allows creative designs.
How long does it take to build a 3D-printed house?
It depends, but most 3D-printed houses are done in 1-2 days. Bigger or more detailed homes might take longer. Still, it’s much faster than regular building methods.
Are 3D-printed houses safe to live in?
Yes, they are safe if built properly. Engineers check the materials and designs to make sure they are strong. But scientists are still studying how long these houses will last.
Can you customize a 3D-printed house?
Yes, you can! 3D printing lets you create special shapes and curved walls. You can work with designers to make a home that matches your style and needs.
Are 3D-printed houses environmentally friendly?
Yes, they are better for the planet. They use fewer materials and make less waste than regular building. Some even use eco-friendly materials, making them a greener choice.




















發表評論
在發布之前,所有評論都會進行調節。
此網站已受到 hCaptcha 保護,且適用 hCaptcha 隱私政策以及服務條款。